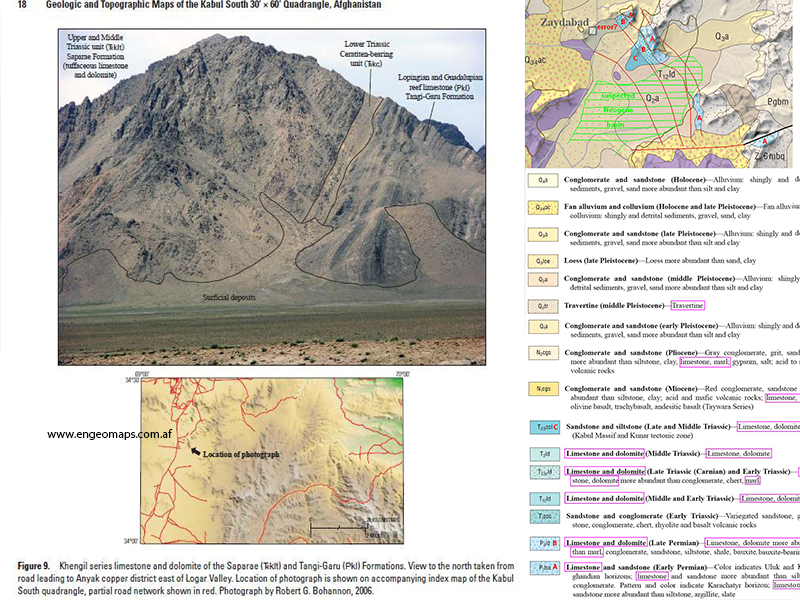
0093-744544394
enquiries@engeomaps.com
-

Environmental Protection
is a practice of protecting the natural environment on individual, organisation controlled or governmental levels, for the benefit of both the environment and humans. Due to the pressures of over consumption, population and technology, the biophysical environment is being degraded, sometimes permanently. This has been recognized, and governments have begun placing restraints on activities that cause environmental degradation. Since the 1960s, activity of environmental movements has created awareness of the various environmental issues. There is no agreement on the extent of the environmental impact of human activity and even scientific dishonesty occurs,.
-
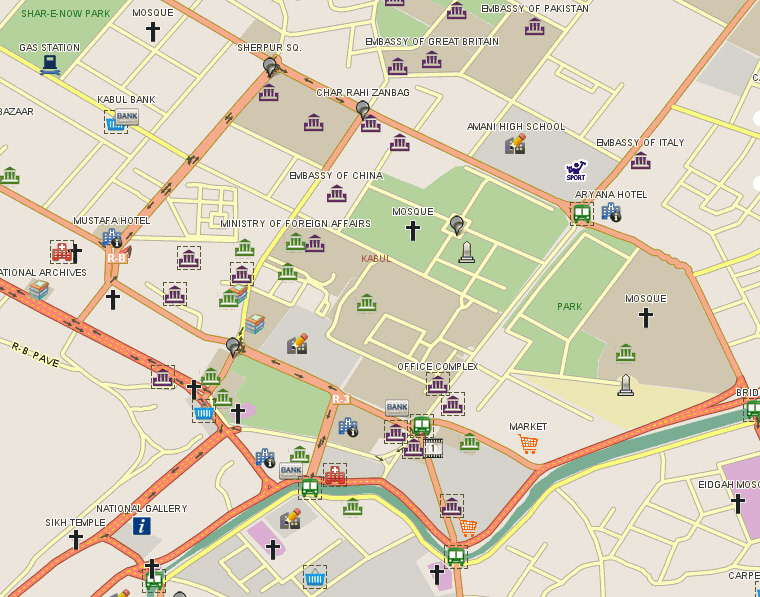
Disaster Management
Disaster management (or emergency management) is the creation of plans through which communities reduce vulnerability to hazards and cope with disasters.Disaster management does not avert or eliminate the threats; instead, it focuses on creating plans to decrease the effect of disasters. Failure to create a plan could lead to human mortality, lost revenue, and damage to assets. Currently in the Afghanistan 90 percent of businesses do not have emergency management plans. Events covered by disaster management include acts of terrorism, industrial sabotage, fire, natural disasters (such as earthquakes, hurricanes, etc.),
-
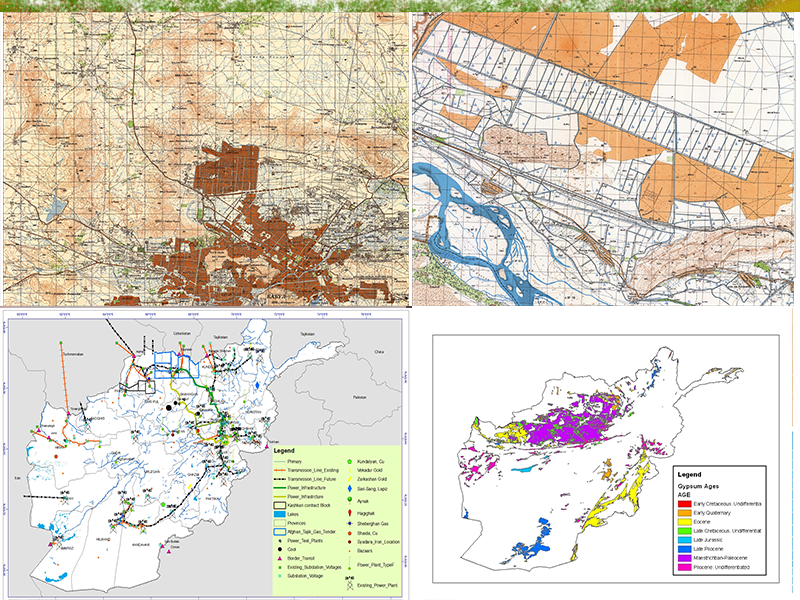
Geo Engineering
is the deliberate and large-scale intervention in the Earth’s climatic system with the aim of limiting adverse climate change.Climate engineering is an umbrella term for two types of measures: carbon dioxide removal and solar radiation management. Carbon dioxide removal addresses the cause of climate change by removing one of the greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide) from the atmosphere. Solar radiation management attempts to offset effects of greenhouse gases by causing the Earth to absorb less solar radiation.Climate engineering approaches are sometimes viewed as additional potential options for limiting climate change, alongside mitigation and adaptation.There is substantial agreement among scientists that climate engineering cannot substitute for climate change mitigation. Some approaches might be used as accompanying measures to sharp cuts in greenhouse gas emissions
-
Environmental Impact assessment
The purpose of the assessment is to ensure that decision makers consider the environmental impacts when deciding whether or not to proceed with a project. The International Association for Impact Assessment (IAIA) defines an environmental impact assessment as "the process of identifying, predicting, evaluating and mitigating the biophysical, social, and other relevant effects of development proposals prior to major decisions being taken and commitments made.
EIAs are unique in that they do not require adherence to a predetermined environmental outcome, but rather they require decision makers to account for environmental values in their decisions and to justify those decisions in light of detailed environmental studies and public comments on the potential environmental impacts